Lyme disease in Domestic Animals | |||
 1,381 1,381  0 0  0 0 | |||
Lyme Disease in Domestic AnimalsLyme disease, a bacterial infection caused by Borrelia burgdorferi (and related species), affects domestic animals, including dogs, cats, and horses. The primary mode of transmission is through the bite of infected blacklegged ticks (deer ticks). While dogs are most frequently diagnosed, the disease's manifestation varies across species.
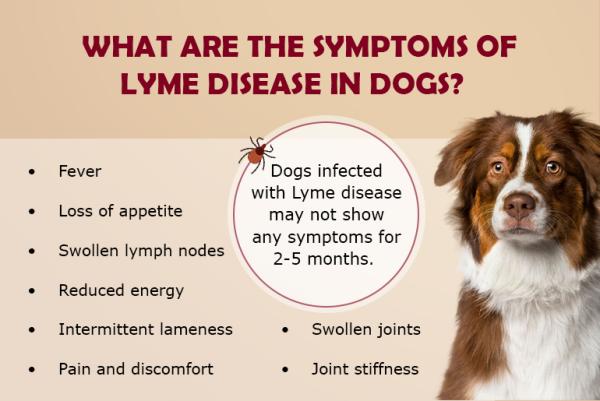
Lyme Disease in DogsDogs are the most commonly affected domestic animals. Symptoms can vary greatly:
Lyme Disease in CatsCats are less susceptible to Lyme disease than dogs and often exhibit subclinical infections (showing few or no symptoms). When symptoms occur, they may resemble those in dogs but are generally less pronounced and harder to diagnose. These can include:
Lyme Disease in HorsesHorses can contract Lyme disease, though it is relatively rare. Symptoms are often subtle:
Diagnosis of Lyme DiseaseDiagnosis in animals involves a combination of the following:
Treatment for Lyme DiseaseTreatment typically involves antibiotics such as doxycycline or amoxicillin. The specific antibiotic and duration will depend on the disease's severity and the animal's overall health.
Prevention of Lyme DiseasePreventative measures are key to protecting pets:
Importance of Veterinary ConsultationIf you suspect your pet has Lyme disease, consult a veterinarian immediately. Early diagnosis and treatment are critical for the best outcome. The provided information is for general knowledge and should not replace professional veterinary advice. Tags: Anorexia Borrelia Burgdorferi Fever Kidney Problems Lameness Lethargy Lyme Disease Lymphadenopathy Skin Lesions Stiffness | |||
| |||
| | |||
|
 3350
3350