Understanding Blackheads (Open Comedones)Blackheads, a common type of acne, occur when a pore becomes clogged with sebum (oil), dead skin cells, and bacteria. The dark appearance isn't dirt, but rather oxidized melanin (skin pigment) that darkens when exposed to air. The clog remains open to the skin's surface. Formation of BlackheadsBlackheads form when pores become blocked with a combination of: - Sebum (Oil): An oily substance produced by sebaceous glands.
- Dead Skin Cells: Cells that haven't properly shed and accumulate.
- Bacteria: Particularly Cutibacterium acnes which contributes to inflammation.
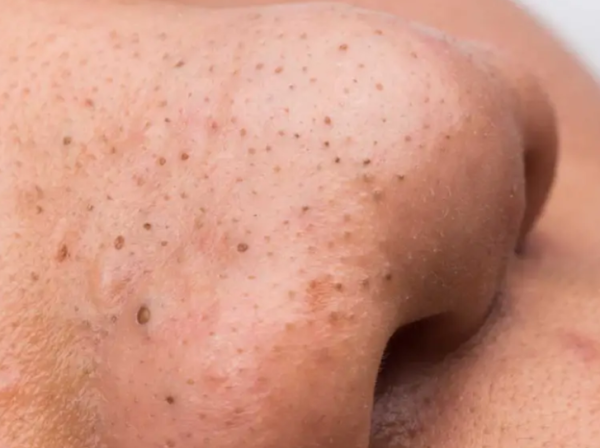
Causes of BlackheadsSeveral factors contribute to blackhead formation: - Excess Sebum Production: Influenced by hormonal changes (puberty, menstruation, pregnancy), genetics, and certain medications.
- Dead Skin Cell Buildup: Skin cells that don't shed properly block pores.
- Bacteria: The bacteria Cutibacterium acnes thrives in clogged pores.
- Genetics: A family history of acne increases susceptibility.
Treatment for BlackheadsTreatment focuses on unclogging pores and preventing future blockages: - Over-the-Counter (OTC) Treatments: Benzoyl peroxide and salicylic acid are effective at killing bacteria and exfoliating dead skin cells.
- Prescription Medications: Topical retinoids (like tretinoin), antibiotics, and azelaic acid can be more potent options.
- Professional Treatments: Chemical peels, microdermabrasion, and extractions (performed by a dermatologist) can help remove blackheads.
Important Note: Squeezing blackheads at home can lead to inflammation, infection, and scarring. Prevention of BlackheadsMaintain a consistent skincare routine: - Gentle Cleansing: Use a mild cleanser twice daily.
- Exfoliation: Exfoliate 1-2 times per week to remove dead skin cells.
- Non-Comedogenic Products: Use products that won't clog pores.
Blackhead ScarringScarring from blackheads, like other acne scarring, can manifest in several forms. Types of Blackhead Scars- Ice Pick Scars: Deep, narrow, pitted scars.
- Boxcar Scars: Wide, u-shaped scars with defined edges.
- Rolling Scars: Wavy, uneven scars that create a bumpy appearance.
- Hyperpigmentation: Dark spots (post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation) that remain after a blackhead heals.
Causes of Blackhead ScarringSevere inflammation from blackheads (or picking at them) can damage the underlying skin tissue, leading to scar formation. The severity of scarring depends on factors like: - Depth and Duration of Inflammation: Deeper and longer inflammation leads to worse scarring.
- Skin Type: Some skin types are more prone to scarring.
- Genetics: Scarring tendencies can be inherited.
Treatment for Blackhead ScarsTreatment options range from topical treatments to more invasive procedures: - Topical Treatments: Retinoids, chemical peels, and certain topical treatments can improve the appearance of scars.
- Microneedling: Stimulates collagen production to improve texture.
- Laser Treatments: Can reduce the appearance of scars.
- Fillers: Can fill in pitted scars.
- Surgical Excision: In severe cases, surgery may be an option.
Important Note on Blackheads and ScarringIf you're struggling with blackheads or acne scarring, consulting a dermatologist is highly recommended. They can accurately diagnose your skin condition, recommend the most appropriate treatment plan, and help you prevent future breakouts and scarring. Self-treating can sometimes worsen the condition.
Tags: Acne Blackhead Scarring Blackheads  
|  1,354
1,354  0
0  0
0  3350
3350 