| Blackheads, a type of acne, occur when dead skin cells and oil clog hair follicles, oxidizing and darkening the trapped sebum (oil). Contributing factors include genetics, hormonal changes, excess oil production (seborrhea), and certain medications. Treatment options range from over-the-counter retinoids and salicylic acid to professional extractions by a dermatologist. Prevention strategies focus on maintaining good skin hygiene through gentle cleansing, exfoliation to remove dead skin cells, and the use of non-comedogenic (non-pore-clogging) products. Consistent skincare and addressing underlying hormonal imbalances can significantly reduce blackhead formation. 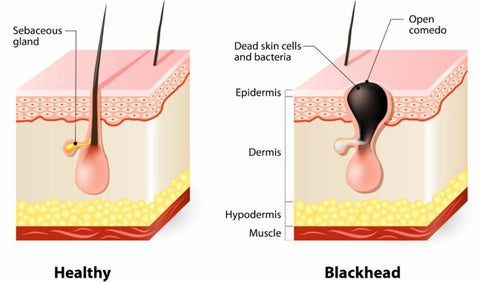
Blackheads, also known as open comedones, are a common type of acne that appears as small, dark bumps on the skin. They're caused by a blockage in the pores, leading to a buildup of sebum (oil), dead skin cells, and bacteria. Unlike whiteheads (closed comedones), the pore remains open, exposing the contents to air, which oxidizes and turns dark. Causes: - Excess sebum production: Oily skin is more prone to blackheads. Hormonal changes, particularly during puberty, pregnancy, or menstruation, can increase sebum production.
- Dead skin cells: The buildup of dead skin cells can clog pores, trapping sebum and creating a breeding ground for bacteria.
- Bacteria: The bacteria *Cutibacterium acnes* (formerly known as *Propionibacterium acnes*) plays a role in the inflammation associated with acne, although it's not the primary cause of blackheads themselves.
- Genetics: A family history of acne increases your risk of developing blackheads.
- Certain medications: Some medications, like corticosteroids and lithium, can contribute to acne.
- Cosmetics and skincare products: Comedogenic (pore-clogging) products can worsen blackheads.
- Friction and pressure: Rubbing or pressing on the skin can irritate pores and contribute to blackhead formation.
Treatment: - Over-the-counter (OTC) treatments:
- Benzoyl peroxide: Kills bacteria and helps unclog pores.
- Salicylic acid: Exfoliates the skin, removing dead skin cells and unclogging pores.
- Retinoids (like retinol): Increase skin cell turnover, preventing pore blockage. Available in various strengths, start with a low concentration.
- AHA/BHA exfoliants: Chemical exfoliants that help remove dead skin cells and unclog pores. Use as directed, as overuse can irritate the skin.
- Professional treatments:
- Microdermabrasion: A procedure that uses tiny crystals or a diamond tip to exfoliate the skin's surface.
- Chemical peels: Chemical solutions are applied to the skin to exfoliate and remove dead skin cells.
- Extractions: A dermatologist or esthetician can manually remove blackheads. Important Note: Attempting to squeeze blackheads at home can worsen inflammation and lead to scarring.
- Lifestyle changes:
- Washing your face twice daily: Use a gentle cleanser appropriate for your skin type.
- Maintaining a healthy diet: While diet's impact on acne is debated, a balanced diet can support overall skin health.
- Managing stress: Stress can worsen acne. Practice stress-reducing techniques like exercise or meditation.
Prevention: - Regular cleansing: Wash your face twice daily with a gentle cleanser.
- Exfoliation: Gently exfoliate 1-2 times per week to remove dead skin cells.
- Use non-comedogenic products: Choose makeup, skincare products, and sunscreens labeled as non-comedogenic or oil-free.
- Avoid touching your face: Hands can transfer bacteria and oil to the skin.
- Keep your hair clean: Oily hair can contribute to blackheads on the forehead and hairline.
- Moisturize: Even oily skin needs moisture. Choose a lightweight, oil-free moisturizer.
- Sunscreen: Use a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher daily.
When to See a Dermatologist:
If over-the-counter treatments don't improve your blackheads or if you experience severe acne, consult a dermatologist. They can provide a personalized treatment plan and address underlying issues. They can also diagnose other skin conditions that might be mimicking blackheads. Remember, consistent and patient care is crucial for managing blackheads and achieving clearer skin.
Tags: Acne Treatment Bacteria Blackheads Dead Skin Cells Genetics Hormonal Changes  
|  1,408
1,408  0
0  0
0  3350
3350 