Exploring Three Vulvar Cancer Treatments | |||
 1,309 1,309  0 0  0 0 | |||
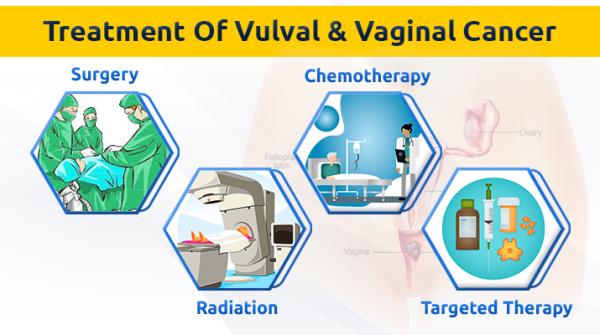
| Three common treatments for vulvar cancer include surgery, which may involve removing the cancerous tissue, lymph nodes, or even the vulva depending on the stage and location of the cancer; radiation therapy, using high-energy beams to kill cancer cells and shrink tumors, often used before or after surgery; and chemotherapy, employing drugs to destroy cancer cells throughout the body, typically used for advanced-stage or recurrent vulvar cancer. The specific treatment plan depends on several factors including the cancer's stage, the patient's overall health, and personal preferences.
Vulvar cancer treatment options depend on several factors including the stage of the cancer, the patient's overall health, and personal preferences. Three common treatments are: 1. Surgery: This is often the primary treatment for vulvar cancer, especially in early stages. The type of surgery depends on the size and location of the tumor, as well as the stage of the cancer. Options include:
2. Radiation Therapy: This uses high-energy radiation to kill cancer cells. It can be used alone or in combination with surgery. External beam radiation therapy delivers radiation from a machine outside the body. Brachytherapy involves placing radioactive sources directly into or near the tumor. Radiation therapy can be used to shrink tumors before surgery, to destroy remaining cancer cells after surgery, or as the primary treatment for patients who are not candidates for surgery. Side effects can include skin irritation, fatigue, and bowel or bladder problems. 3. Chemotherapy: This uses drugs to kill cancer cells. It's usually used for advanced-stage vulvar cancer that has spread to other parts of the body or for recurrent vulvar cancer. Chemotherapy can be given intravenously (through a vein) or orally (by mouth). It can be used alone or in combination with radiation therapy. Side effects can vary greatly depending on the specific drugs used but can include nausea, vomiting, hair loss, fatigue, and decreased blood cell counts. It's crucial to remember that this is not an exhaustive list and the specific treatment plan will be developed by a team of healthcare professionals, including a gynecologic oncologist, based on an individual patient's diagnosis and circumstances. Patients should discuss all treatment options and potential side effects with their doctor to make informed decisions. Tags: Cancer Treatment Chemotherapy Medical Procedures Oncology Patient Care Radiation Therapy Surgery Vaginal Cancer Vaginal Cancer Treatement Valval Cancer Valval Cancer Treatement Vulvar Cancer | |||
| |||
| | |||
|
 3350
3350