The Looming Threat: Stomach Cancer and its Ties to Tobacco and Alcohol Abuse | |||
 1,381 1,381  0 0  0 0 | |||
| Stomach cancer, a significant global health concern, is strongly linked to both tobacco and alcohol abuse. Smoking damages the stomach lining, increasing the risk of inflammation and precancerous changes, while excessive alcohol consumption irritates the stomach and can lead to the development of Helicobacter pylori infections, a known risk factor for stomach cancer. The combined effect of tobacco and alcohol use dramatically elevates the risk, highlighting the importance of avoiding these substances to reduce the likelihood of developing this potentially deadly disease.
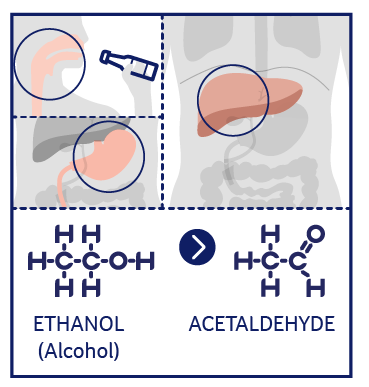
Stomach cancer, a malignancy affecting the lining of the stomach, remains a significant global health concern. While its exact causes are multifaceted and not fully understood, a strong correlation exists between its development and the abuse of tobacco and alcohol. This link underscores the critical importance of preventative measures centered around reducing or eliminating these harmful habits. The Tobacco Connection: Smoking significantly increases the risk of stomach cancer. The carcinogens in tobacco smoke directly damage the stomach lining, creating an environment conducive to cancerous cell growth. Furthermore, smoking can impair the stomach's protective mucus layer, making it more vulnerable to irritation and inflammation, potential precursors to cancer. The increased risk is observed even with passive smoking, highlighting the pervasive danger of tobacco exposure. The Alcohol Link: Heavy alcohol consumption is another major risk factor. Alcohol's corrosive effects irritate the stomach lining, leading to chronic inflammation and potentially precancerous lesions. The interaction between alcohol and tobacco further exacerbates this risk, creating a synergistic effect that significantly increases the likelihood of developing stomach cancer. Acetaldehyde, a toxic byproduct of alcohol metabolism, is also a known carcinogen. Beyond Tobacco and Alcohol: While tobacco and alcohol abuse are significant contributors, other factors increase the risk of stomach cancer, including:
The Looming Threat: The combined effect of tobacco and alcohol abuse significantly amplifies the risk of stomach cancer, making it a particularly serious threat for individuals engaging in these habits. Early detection is crucial for successful treatment, emphasizing the importance of regular health check-ups and screenings, especially for those with risk factors. Conclusion: Reducing or eliminating tobacco and alcohol use is a crucial step in mitigating the risk of stomach cancer. Adopting a healthy lifestyle that includes a balanced diet, regular exercise, and addressing other risk factors like H. pylori infection, significantly improves the chances of preventing this potentially fatal disease. Public health initiatives focusing on education and cessation programs are vital in combating this looming threat. Tags: Alchol Consumption Alcohol Abuse Helicobacter Pylori Stomach Cancer Tobacco 간암 담배 | |||
| |||
| | |||
|
 3350
3350