| Stomach cancer, also known as gastric cancer, is a malignant tumor that arises in the lining of the stomach. It's a relatively common cancer globally, with variations in incidence rates depending on geographic location and dietary factors. Risk factors include infection with Helicobacter pylori, smoking, a diet high in processed meats and low in fruits and vegetables, pernicious anemia, and a family history of the disease. Symptoms can be vague and often don't appear until the cancer is advanced, including abdominal pain, indigestion, weight loss, nausea, and vomiting. Diagnosis involves endoscopy and biopsy, with treatment options including surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and targeted therapy depending on the stage and type of cancer. 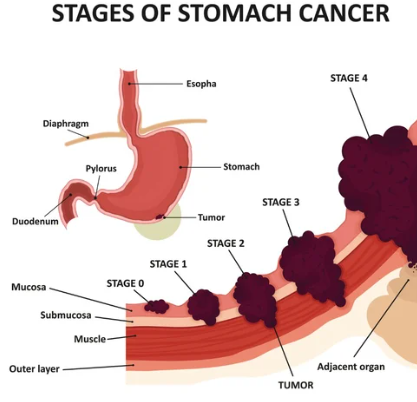
Stomach cancer, also known as gastric cancer, is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the lining of the stomach. It's a significant global health problem, although its incidence has been declining in many developed countries.
Causes: The exact cause of stomach cancer isn't fully understood, but several risk factors are identified:- Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection: This bacteria is a major risk factor, increasing the risk of both stomach ulcers and stomach cancer.
- Diet: Diets low in fruits and vegetables and high in processed meats and salted foods are associated with increased risk. Smoking and alcohol consumption also play a role.
- Genetics: A family history of stomach cancer increases risk. Specific genetic mutations can also predispose individuals.
- Age: Risk increases significantly with age, with most cases occurring after age 50.
- Achlorhydria: Lack of stomach acid production.
- Certain medical conditions: Conditions like pernicious anemia (vitamin B12 deficiency) and atrophic gastritis (inflammation and thinning of the stomach lining) are linked to an increased risk.
- Previous stomach surgery: A history of stomach surgery, especially for ulcers or polyps, may increase the risk.
Symptoms: Symptoms can be vague and often appear in later stages. They may include:- Abdominal pain or discomfort: Often described as a burning sensation or gnawing pain in the upper abdomen.
- Indigestion or heartburn: Persistent and worsening indigestion or heartburn.
- Nausea and vomiting: Recurring nausea and vomiting, possibly with blood.
- Loss of appetite and unintentional weight loss: Significant weight loss without trying.
- Feeling full quickly after eating (early satiety): Difficulty eating full meals due to feeling full.
- Bloating: Frequent bloating and abdominal distension.
- Fatigue: Unexplained tiredness and weakness.
- Anemia: Due to bleeding from the stomach.
- Black or bloody stools (melena): Indicative of internal bleeding.
- Vomiting blood (hematemesis): A serious sign of bleeding.
Diagnosis: Diagnosis typically involves:- Physical examination: A doctor will examine the abdomen and check for any abnormalities.
- Endoscopy: A procedure using a thin, flexible tube with a camera to visualize the stomach lining. Biopsies may be taken during endoscopy.
- Imaging tests: Such as CT scans, MRI scans, or ultrasound, to assess the extent of the cancer.
- Blood tests: To check for anemia and other abnormalities.
Treatment: Treatment options depend on the stage and type of stomach cancer and may include:- Surgery: To remove the cancerous portion of the stomach.
- Chemotherapy: Using drugs to kill cancer cells.
- Radiation therapy: Using high-energy radiation to kill cancer cells.
- Targeted therapy: Drugs that target specific molecules involved in cancer growth.
- Immunotherapy: Stimulates the body's immune system to fight cancer cells.
Stomach Cancer Prevention:While not all cases can be prevented, reducing risk factors such as H. pylori infection (through treatment and hygiene), maintaining a healthy diet, avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, and regular health checkups can help.
This information is for general knowledge only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult a healthcare professional for any health concerns or before making any decisions related to your health or treatment.
Tags: Biopsy Chemotherapy Endoscopy Gastric Cancer Helicobacter Pylori Pernicious Anemia Radiation Therapy Smoking Stomach Cancer Stomach Cancer Prevention Targeted Therapy 위암  
|  1,393
1,393  0
0  0
0  3350
3350 