| Hodgkin's disease treatment depends on the stage and type of the disease, as well as the patient's overall health. Common treatments include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and in some cases, targeted therapy, immunotherapy, or a combination of these. For early-stage disease, radiation therapy might be sufficient, while advanced-stage Hodgkin's lymphoma usually requires a combination of chemotherapy and radiation. Stem cell transplantation may be an option for patients who don't respond to initial treatments or experience relapse. 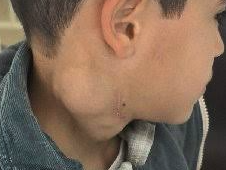
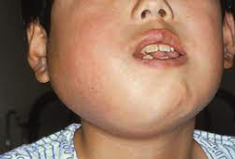
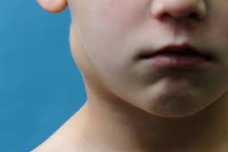
Hodgkin's lymphoma (Hodgkin's disease) treatment depends on several factors, including the stage of the cancer, the patient's age and overall health, and the specific type of Hodgkin lymphoma. Treatment typically involves a combination of approaches, and the best course will be determined by a medical oncologist or hematologist. Common treatments include: - Chemotherapy: This is a cornerstone of Hodgkin's lymphoma treatment. Various chemotherapy drugs are used, often in combination, to kill cancerous cells. The specific drugs and regimens vary depending on the stage and other factors. Examples include ABVD (doxorubicin, bleomycin, vinblastine, and dacarbazine) and BEACOPP (bleomycin, etoposide, doxorubicin, cyclophosphamide, vincristine, procarbazine, and prednisone).
- Radiation Therapy: This uses high-energy radiation to target and destroy cancer cells. It's often used in combination with chemotherapy, especially in early-stage Hodgkin's lymphoma. Radiation therapy can be delivered externally (external beam radiation therapy) or internally (brachytherapy, though less common in Hodgkin's).
- Targeted Therapy: Drugs like brentuximab vedotin (Adcetris) target specific proteins on Hodgkin lymphoma cells, helping to kill them while minimizing harm to healthy cells. This is often used in relapsed or refractory disease (disease that hasn't responded to other treatments).
- Immunotherapy: This harnesses the body's own immune system to fight cancer cells. Examples include checkpoint inhibitors (like nivolumab or pembrolizumab) which block signals that prevent the immune system from attacking cancer cells, and monoclonal antibodies like brentuximab vedotin (mentioned above).
- Stem Cell Transplant (Bone Marrow Transplant): This is a more intensive treatment reserved for patients whose disease hasn't responded to other treatments or has relapsed. It involves high-dose chemotherapy or radiation to destroy cancerous cells, followed by the transplantation of healthy stem cells (often from the patient's own blood or bone marrow) to restore blood cell production.
The specific treatment plan is highly individualized. Factors considered include: - Stage: Early-stage Hodgkin lymphoma often responds well to radiation therapy alone or in combination with chemotherapy. Advanced-stage disease usually requires more intensive combination chemotherapy.
- Patient's Age and Overall Health: Older patients or those with other health conditions might receive less intensive treatment.
- Type of Hodgkin Lymphoma: There are different subtypes of Hodgkin lymphoma, and treatment may be tailored accordingly.
It's crucial to discuss treatment options thoroughly with a medical oncologist or hematologist specializing in lymphoma. They can assess your individual situation and recommend the most appropriate and effective treatment plan.
Tags: Chemotherapy Hodgkin's Disease Hodgkin's Lymphoma Hodgkin's Lymphoma Therapy Hodgkin's Lymphoma Treatment Immunotherapy Radiation Therapy 림프종 림프종 진단 림프종 치료 호지킨 림프종  
|  1,401
1,401  0
0  0
0  3350
3350 

