Navigating the Road to Recovery - How is Impetigo Treated? | |||
 2,230 2,230  0 0  0 0 | |||
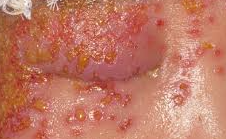
| Impetigo is a highly contagious bacterial skin infection, most commonly caused by *Staphylococcus aureus* or *Streptococcus pyogenes*, characterized by sores that rupture, forming a honey-colored crust. It primarily affects infants and children, often appearing on the face, hands, and diaper area. Treatment usually involves topical antibiotics, though oral antibiotics may be necessary for severe cases. Good hygiene practices, such as handwashing and avoiding contact with infected individuals, are crucial in preventing its spread.
Causes: Impetigo is most often caused by two bacteria: Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes. These bacteria typically enter the body through a break in the skin, such as a scratch or insect bite. The infection spreads easily through direct contact with an infected person or contaminated objects.
Treatment: Impetigo is usually treated with topical antibiotics (creams or ointments) applied directly to the sores. In more severe cases, oral antibiotics may be prescribed. Good hygiene practices, such as frequent handwashing and keeping the affected area clean and dry, are crucial to prevent the spread of the infection.
Prevention: Good hygiene is key to preventing impetigo. This includes:
If you suspect your child or yourself has impetigo, it's important to consult a doctor for diagnosis and treatment. Early treatment helps prevent the spread of the infection and reduces the risk of complications. Tags: Bacterial Skin Infection Bullous impetigo Impetigo Staphylococcus Aureus Streptococcus Pyogenes 농가진 | |||
| |||
| | |||
|
 3350
3350