What is Lyme Disease? | |||
 1,450 1,450  0 0  0 0 | |||
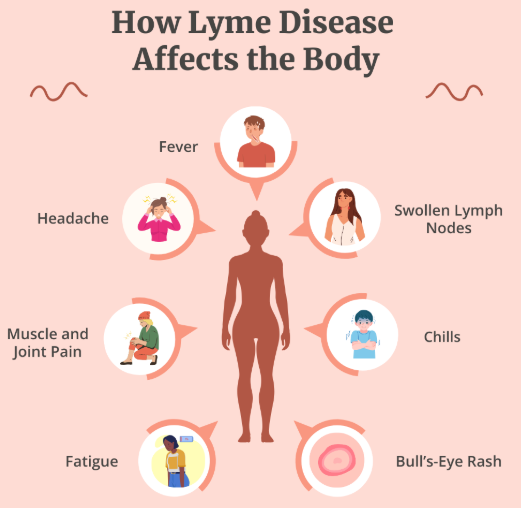
| Lyme disease is a bacterial infection transmitted to humans through the bite of infected blacklegged ticks. The bacteria responsible is Borrelia Burgdorferi (and in some areas, related species). If left untreated, the infection can spread to joints, the heart, and the nervous system. Early symptoms often include a characteristic skin rash (erythema migrans), fever, headache, fatigue, and muscle aches. Later symptoms can be more varied and severe.
Lyme Disease Symptoms can vary widely depending on the stage of infection. They're also often nonspecific, meaning they can mimic other illnesses, making diagnosis challenging. Symptoms are categorized into early localized, early disseminated, and late disseminated stages:
Early Disseminated Stage (weeks to months after the tick bite):
Late Disseminated Stage (months to years after the tick bite):
Important Note: Many people with Lyme disease don't experience all of these symptoms, and some may have very mild or subtle symptoms. If you suspect you may have Lyme disease, it's crucial to seek medical attention promptly. Early diagnosis and treatment are key to preventing long-term complications. A blood test is often used to help diagnose Lyme disease, but it's not always accurate in the early stages of infection. Tags: Blood meal Borrelia Borrelia Afzelii Borrelia Bacteria Dermacentor Variabilis Lyme Borreliosis Lyme Disease Spirochaetes Spirochete Bacteria | |||
| |||
| | |||
|
 3354
3354