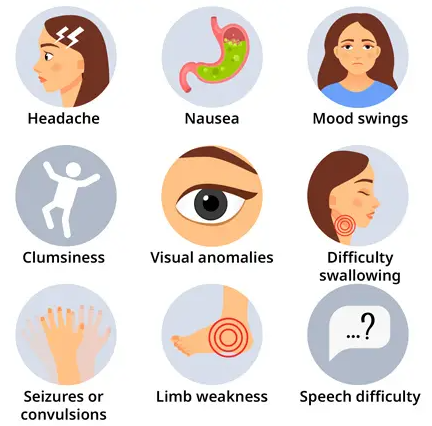
| Brain tumor symptoms are highly variable, depending on the size and specific location of the tumor within the brain. These symptoms arise primarily from two mechanisms: direct damage to essential brain tissue and increased pressure caused by the tumor itself or associated swelling. This pressure can occur when the tumor obstructs the normal flow of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), leading to a buildup of pressure within the skull. Common SymptomsSeveral common symptoms may indicate the presence of a brain tumor. These should be evaluated by a medical professional for proper diagnosis. - Headaches: Headaches associated with brain tumors often exhibit a distinctive pattern. They tend to be more severe in the morning and may gradually worsen over time.
- Seizures: Seizures can manifest as a result of abnormal electrical activity in the brain, often triggered by the presence of a tumor.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Persistent nausea and vomiting, particularly when unexplained by other medical conditions, can be symptoms.
- Weakness or Loss of Feeling: Weakness or numbness in the arms or legs can indicate that the tumor is affecting areas of the brain that control motor function or sensory perception. These symptoms may be one-sided, impacting only one side of the body.
- Stumbling or Lack of Coordination: Difficulty with balance and coordination while walking, often described as stumbling or clumsiness, suggests the tumor may be impacting the cerebellum, which controls motor skills.
- Abnormal Eye Movements or Changes in Vision: Changes in vision, such as blurred vision, double vision, or loss of peripheral vision, as well as abnormal eye movements, may occur due to pressure on or damage to the optic nerves or areas of the brain responsible for vision control.
- Drowsiness: Excessive drowsiness or lethargy can be a sign of increased pressure within the skull.
- Changes in Personality or Memory: Cognitive changes such as altered personality, confusion, memory loss, or difficulty concentrating can also occur as a result of damage to the brain from the tumor.
- Changes in Speech: Speech difficulties such as slurred speech, difficulty finding words, or trouble understanding language can indicate a tumor affecting language centers in the brain.
Tags: Ateriogram Brain Cancer Brain Scan Brain Tumors Calcium Cancer Cell Genetic Aspect Headache Malignant Brain Tumor Nausea Seizures Smelling Speech Vomitting  
|  1,588
1,588  0
0  0
0  3354
3354 