| The simplest way to mask your IP address on a home network is to use a Virtual Private Network (VPN). A VPN encrypts your internet traffic and routes it through a VPN server, masking your actual IP address with the server's IP address. To do this, choose a reputable VPN provider, download and install their software, create an account, and connect to a server location of your choice. Your online activity will then appear to originate from the VPN server's location, not your home network. 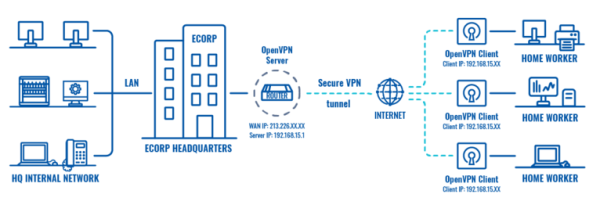
Masking your IP address on a home network involves using a VPN (Virtual Private Network) or a proxy server. Here's a simplified breakdown of each:
Method 1: Using a VPN (Recommended)1. Choose a VPN provider: Research reputable VPN providers. Look for features like strong encryption, a no-logs policy, and a wide server network. Many offer free trials or limited free plans to test before committing. Examples include NordVPN, ExpressVPN, Surfshark (but countless others exist).
2. Download and install the VPN software: Download the VPN app from the provider's website for your operating system (Windows, macOS, Android, iOS, etc.).
3. Create an account and log in: Follow the provider's instructions to create an account and log in to the app.
4. Connect to a server: Choose a server location from the VPN's list. Connecting to a server in a different country will mask your IP address with that server's IP address.
5. Verify your IP address: Use a website like whatismyip.com to confirm your IP address has changed to the VPN server's IP.
Method 2: Using a Proxy Server (Less Secure)Proxy servers are generally less secure than VPNs. They only mask your IP for the specific application you're using them with, and may not encrypt your connection.
1. Choose a proxy server: Find a reliable proxy server provider. Be cautious, as many free proxy servers are unreliable or insecure.
2. Configure your device: The method for configuring a proxy server varies depending on your operating system and the application you're using. You'll typically need to enter the proxy server's IP address and port number in your system's network settings or within the application itself.
3. Verify your IP address: Use a website like whatismyip.com to check if your IP has changed.
Important Considerations:- Security: VPNs are generally more secure than proxy servers, offering encryption to protect your data. Choose a reputable VPN provider with a strong track record.
- Speed: Both VPNs and proxies can slow down your internet speed. The impact depends on factors like server location and network congestion.
- Legality: The legality of using VPNs and proxies varies depending on your location and how you use them. Some countries restrict or prohibit their use. Always check your local laws and regulations.
- Cost: While some free VPNs and proxy servers exist, paid services often provide better security, speed, and reliability.
This information is for educational purposes only. Always exercise caution when sharing your personal information online and choose services with a strong reputation.
Tags: ARP Cache Poisoning Home Networking IP Spoofing Network Security Privacy VPN Virtual Private Network  
|  2,663
2,663  0
0  0
0  3350
3350 