| The central nervous system (CNS), comprising the brain and spinal cord, acts as the body's command center, receiving, processing, and transmitting information to coordinate virtually all bodily functions. The brain, responsible for higher-level cognitive functions like thought and emotion, receives sensory input, interprets it, and initiates motor responses. The spinal cord serves as the primary communication pathway between the brain and the rest of the body, relaying sensory information to the brain and transmitting motor commands to muscles and glands. This intricate interplay ensures rapid responses to internal and external stimuli, maintaining homeostasis and enabling conscious and unconscious actions. 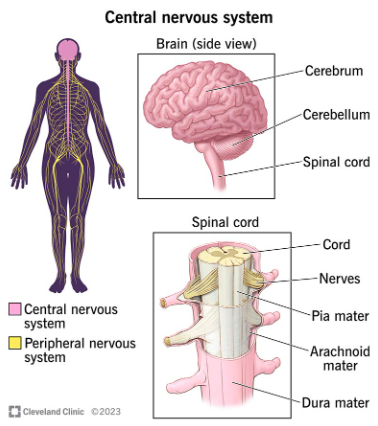
The central nervous system (CNS) is the body's command center, responsible for receiving, processing, and transmitting information. It's the crucial link between our internal world and our external environment, allowing us to interact with the world and maintain internal balance (homeostasis). Understanding its functions demystifies its importance in our daily lives. Let's break it down: - Sensory Input: The CNS's primary function begins with gathering information. Specialized sensory receptors throughout the body (eyes, ears, skin, etc.) detect stimuli – light, sound, pressure, temperature, pain, and chemical changes. This sensory information is then converted into electrical signals that travel along nerves to the CNS.
- Integration and Processing: The brain and spinal cord, the two main components of the CNS, receive this sensory input. They then process this information, interpreting its meaning, and making decisions about how to respond. This involves complex interactions between billions of neurons, creating intricate neural networks that analyze the data, compare it to past experiences, and formulate a response.
- Motor Output: Based on the processed information, the CNS generates appropriate responses. This involves sending signals along motor neurons to muscles and glands. These signals initiate actions like movement, glandular secretions (hormones), and changes in organ function. This ensures our body reacts appropriately to both internal and external stimuli.
- Maintaining Homeostasis: The CNS plays a crucial role in regulating internal body conditions, keeping them within a narrow range optimal for survival. This includes maintaining body temperature, blood pressure, heart rate, and respiration. The hypothalamus, a region in the brain, is particularly important in this regulatory function.
- Higher-Level Functions: Beyond basic survival mechanisms, the CNS is responsible for a range of sophisticated functions that define our humanity:
- Cognition: This includes thinking, learning, memory, problem-solving, and language. Different regions of the brain specialize in these cognitive processes.
- Emotions: The limbic system, a network of brain structures, plays a crucial role in processing and regulating emotions like fear, joy, anger, and sadness.
- Consciousness: The exact mechanisms are still being researched, but the CNS underlies our awareness of ourselves and our surroundings.
- Personality: The complex interplay of different brain regions and their interactions shape our individual personalities.
Components of the CNS:- Brain: The main processing center, divided into several regions with specialized functions (cerebrum, cerebellum, brainstem).
- Spinal Cord: A long, cylindrical structure that transmits information between the brain and the rest of the body. It also plays a role in reflexes – rapid, involuntary responses to stimuli.
Dysfunction of the CNS:Damage to the CNS, whether from injury, disease (e.g., stroke, multiple sclerosis, Alzheimer's disease), or genetic disorders, can have devastating consequences, affecting everything from basic motor functions to complex cognitive abilities.
Understanding the vital functions of the CNS highlights its critical role in our health and well-being. Its intricate workings continue to be a focus of intense scientific research, constantly revealing new insights into the complexity and wonder of the human nervous system.
Tags: Anatomy Brain Central Nervous System Cognitive Functions Health Education Medical Science Neuroscience Physiology Spinal Cord  
|
 2,494
2,494  2,494
2,494  2,497
2,497  0
0  0
0