| Side effects of endocrine cancer treatment, which often involves hormone therapy, surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, or targeted therapy, vary depending on the specific treatment and the individual. Common side effects can include fatigue, nausea, vomiting, hair loss, weight changes (gain or loss), hot flashes, night sweats, bone pain, changes in libido, depression, anxiety, and decreased fertility or infertility. More serious side effects, though less common, may involve cardiovascular problems, blood clots, kidney or liver damage, and increased risk of infection. The severity and duration of these side effects also vary greatly. 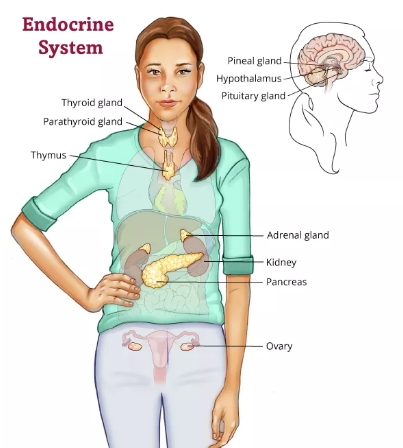
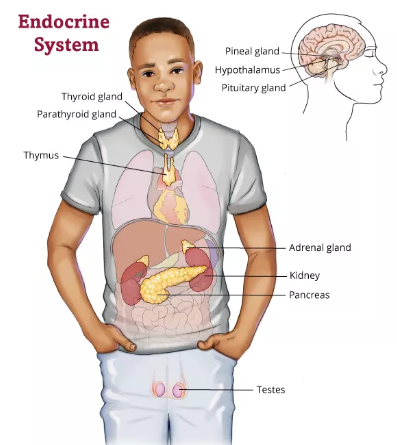
The side effects of endocrine cancer treatment vary greatly depending on the specific type of cancer (e.g., thyroid, adrenal, pituitary), the stage of the cancer, and the type of treatment received. Common treatments include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, hormone therapy, and radioiodine therapy. Side effects can range from mild and temporary to severe and long-lasting.
General Side Effects (can occur with multiple treatments): - Fatigue: This is a very common side effect of many cancer treatments.
- Nausea and vomiting: Often managed with anti-nausea medication.
- Hair loss (alopecia): More common with chemotherapy, but can also occur with radiation.
- Weight changes: Both weight gain and weight loss are possible.
- Skin changes: Radiation can cause skin irritation, dryness, and redness. Chemotherapy can cause skin rashes or increased sensitivity to sunlight.
- Mouth sores (mucositis): Can be painful and make eating difficult.
- Constipation or diarrhea: Common gastrointestinal side effects.
- Cognitive changes ("chemo brain"): Difficulty with concentration, memory, and other cognitive functions. This can occur with various treatments, but is especially associated with chemotherapy.
- Depression and anxiety: The stress of a cancer diagnosis and treatment can significantly impact mental health.
Treatment-Specific Side Effects: - Surgery: Specific side effects depend on the location and extent of surgery. Possible side effects include pain, infection, scarring, and potential damage to nearby organs or nerves. For example, thyroid surgery can lead to hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) requiring lifelong hormone replacement. Pituitary surgery can affect hormone production leading to various hormonal imbalances.
- Radiation Therapy: Can cause fatigue, skin reactions, nausea, and potentially long-term organ damage depending on the area treated.
- Chemotherapy: A wide range of side effects is possible, including those listed above, as well as bone marrow suppression (leading to increased risk of infection and bleeding), neuropathy (nerve damage), and infertility.
- Targeted Therapy: Side effects vary widely depending on the specific drug, but can include fatigue, skin rashes, diarrhea, hypertension, and others.
- Hormone Therapy: Aims to block or suppress hormone production, which can lead to significant side effects depending on the hormones involved. These can include hot flashes, weight changes, mood swings, decreased libido, bone loss (osteoporosis), and cardiovascular problems.
- Radioiodine Therapy: Can cause temporary thyroid pain and swelling, and salivary gland problems (dry mouth).
Important Note: This is not an exhaustive list, and the severity and type of side effects experienced will vary from person to person. It's crucial to discuss potential side effects with your oncologist before starting any treatment. They can help manage side effects and develop a plan to minimize their impact on your quality of life. Early reporting of side effects to your healthcare team is essential for effective management.
Tags: Anxiety Bone Pain Changes in Libido Decreased Fertility Depressionn Endocrine Cancer Fatigue Hair Loss Hot Flashes Infertility Nausea Night Sweats Side Effects of Endocrine Cancer Vomiting Weight Changes  
|
 1,246
1,246  0
0  0
0  3354
3354 
