| Surgery for spine tumors aims to remove the tumor, stabilize the spine, and relieve nerve compression. The specific surgical approach depends on the tumor's location, size, type, and the patient's overall health, ranging from minimally invasive procedures like biopsies or tumor debulking to extensive surgeries involving spinal fusion or instrumentation for stability. Post-operative care typically includes pain management, rehabilitation, and ongoing monitoring for tumor recurrence. 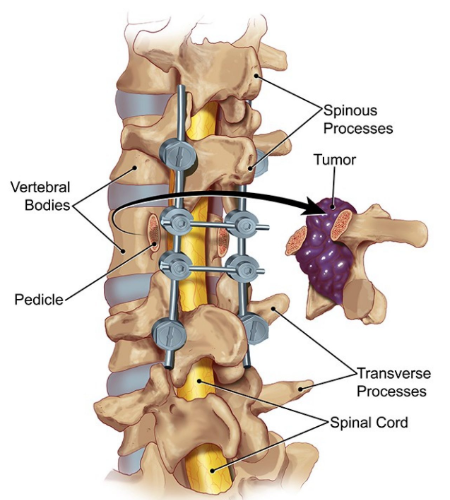
Surgery for spine tumors is a complex field with approaches varying greatly depending on the type, location, and size of the tumor, as well as the patient's overall health. The goal of surgery is to remove as much of the tumor as possible while minimizing damage to the spinal cord and surrounding nerves. This may involve complete removal (resection), partial removal (debulking), or biopsy alone.
Types of Spine Tumor Surgery:- Laminectomy: This involves removing a portion of the lamina (the bony arch of the vertebra) to relieve pressure on the spinal cord or nerves. It's often used for tumors that are primarily compressing the spinal cord but not directly invading the vertebra itself.
- Laminoplasty: Similar to a laminectomy, but instead of removing the lamina, it's spread open and then closed with small plates. This approach preserves more of the bone structure, potentially leading to better stability and less risk of post-surgical instability.
- Vertebrectomy: This involves the removal of all or part of a vertebra. It's typically used for tumors that have invaded the vertebra itself. Reconstruction with bone grafts or implants is usually necessary afterwards to maintain spinal stability.
- Spinal Fusion: This procedure joins two or more vertebrae together to stabilize the spine after a vertebrectomy or other procedures that compromise stability. Bone grafts or metal implants are used to aid in the fusion process.
- Corpectomy: This involves the removal of the vertebral body (the main part of the vertebra). This is a more extensive procedure than a vertebrectomy and requires significant reconstruction to maintain spinal alignment and stability.
- Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery (MISS): This approach utilizes smaller incisions, resulting in less tissue trauma, reduced blood loss, shorter hospital stays, and faster recovery times. However, not all spinal tumors are amenable to MISS.
- Stereotactic Radiosurgery (SRS) and Gamma Knife Radiosurgery: These non-invasive techniques use highly focused beams of radiation to target the tumor, minimizing damage to surrounding tissues. They are often used for smaller tumors or in conjunction with surgery.
Factors influencing surgical approach:- Type of tumor: Benign tumors often require less aggressive surgery than malignant tumors.
- Location of tumor: Tumors in the spinal canal require different surgical techniques than tumors in the vertebral body.
- Size of tumor: Larger tumors may require more extensive surgery.
- Patient's overall health: The patient's age, overall health, and other medical conditions will influence the surgeon's decision on the best surgical approach.
Risks of Spine Tumor Surgery:- Bleeding: Surgery always carries a risk of bleeding.
- Infection: Infection can occur at the surgical site.
- Nerve damage: Damage to nerves can result in weakness, numbness, or paralysis.
- Spinal instability: Surgery can sometimes lead to instability of the spine.
- Cerebrospinal fluid leak: This can cause headaches and other complications.
- Death: Though rare, surgery carries the risk of death.
Post-operative care:Post-operative care includes pain management, physical therapy, and monitoring for complications. The recovery period varies greatly depending on the type and extent of surgery.
This information is for general knowledge only and should not be considered medical advice. Always consult with a qualified medical professional for diagnosis and treatment of spine tumors. A neurosurgeon or orthopedic spine surgeon specializing in spinal oncology is best suited to manage these complex cases.
Tags: Corpectomy Laminectomy Laminoplasty Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery Spinal Fusion Spine Tumor Surgery Spine Tumors Sppinal Cord Stereotactic Radiosurgery Vertebrectomy  
|  1,323
1,323  0
0  0
0  3350
3350 