| Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) is a precise radiation therapy technique used to treat brain tumors and other lesions. It delivers a highly focused, high-dose radiation beam to the targeted area, minimizing damage to surrounding healthy brain tissue. Unlike traditional radiation therapy which involves multiple treatments over several weeks, SRS typically delivers the entire radiation dose in a single session or a few precisely planned sessions. This precision allows for effective tumor control while reducing side effects associated with more invasive procedures like surgery. 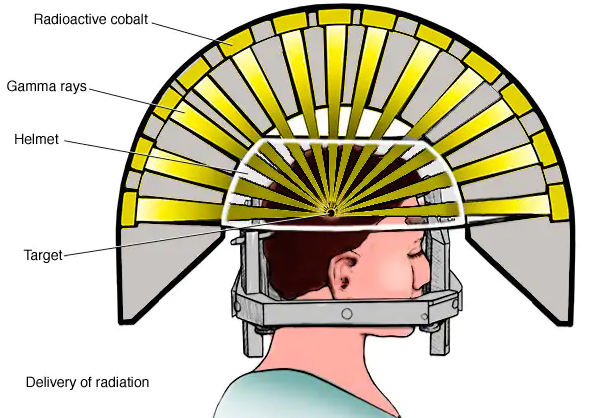 ![]()
Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) is a highly precise form of radiation therapy used to treat brain tumors and other abnormalities in the brain. Unlike traditional radiation therapy, which delivers radiation over several weeks, SRS delivers a highly concentrated dose of radiation to a very small, targeted area in a single session or a few sessions. This precision minimizes damage to surrounding healthy brain tissue.
How it Works:
SRS uses advanced imaging techniques, such as MRI and CT scans, to pinpoint the location of the tumor with extreme accuracy. This information is then used to plan the radiation delivery. Several different types of SRS technologies exist, including: - Linear Accelerator (LINAC) based SRS: This is the most common type, using a sophisticated linear accelerator to deliver precisely aimed beams of radiation.
- Gamma Knife: This system uses multiple sources of gamma radiation focused on the tumor from various angles.
- CyberKnife: This robotic system allows for real-time tracking of the tumor and adjustments to the radiation beams during treatment, compensating for any movement.
Regardless of the technology used, the goal remains the same: to deliver a high dose of radiation to the tumor while sparing surrounding healthy tissue. This is achieved through sophisticated planning and precise delivery of radiation.
Benefits of SRS: - High Precision: SRS delivers radiation with pinpoint accuracy, minimizing damage to healthy brain tissue.
- Non-invasive: It's a non-surgical procedure, meaning there's no need for an incision or general anesthesia.
- Shorter Treatment Time: Treatment is typically completed in a single session or a few short sessions, compared to weeks of traditional radiation therapy.
- Outpatient Procedure: Most SRS procedures can be performed on an outpatient basis, minimizing hospital stays.
- Fewer Side Effects: Due to its precision, SRS generally causes fewer side effects than traditional radiation therapy.
Potential Side Effects:
While SRS is generally safe and effective, potential side effects can include: - Brain Swelling: This is relatively common and can be managed with medication.
- Headaches: These are often mild and temporary.
- Fatigue: Feeling tired is a common side effect.
- Radiation Necrosis: In rare cases, the radiated tissue can die, causing neurological problems. The risk is generally low, but it depends on several factors, including tumor type and location.
- Cognitive Changes: Some patients may experience changes in memory or cognitive function, though this is also rare.
Who is a Candidate for SRS?
SRS is a suitable treatment option for various brain tumors and lesions, including: - Small brain metastases (tumors that have spread from another part of the body): This is a common application of SRS.
- Benign brain tumors: SRS can be used to treat certain types of benign tumors.
- Arteriovenous malformations (AVMs): SRS can help to close off abnormal blood vessels.
- Trigeminal neuralgia: SRS can alleviate the pain associated with this nerve disorder.
Conclusion:
Stereotactic radiosurgery is a powerful and precise treatment option for various brain conditions. Its ability to target tumors with high accuracy while minimizing damage to healthy tissue makes it a valuable tool in the fight against brain tumors. However, it's crucial to discuss the risks and benefits with a qualified neurosurgeon or radiation oncologist to determine if SRS is the right treatment for your specific situation.
Tags: Brain Tumor Treatment Brain Tumors Precise Radiation Therapy Radiation Therapy Radiosurgery SRS Stereotactic Radiosurgery  
|  1,433
1,433  0
0  0
0  3350
3350 