| Chemotherapy for brain cancer involves using drugs to kill cancer cells, but its effectiveness is limited by the blood-brain barrier, which restricts drug passage into the brain. Treatment typically involves systemic chemotherapy (drugs delivered intravenously or orally), which may reach some brain tumors, and sometimes intrathecal chemotherapy (drugs injected directly into the cerebrospinal fluid) to target cancers spread within the fluid. The specific chemotherapy regimen depends on the type and location of the brain cancer, its aggressiveness, and the patient's overall health, with options including temozolomide, carmustine, lomustine, and others, often used in combination or sequentially. Response rates and side effects vary widely. 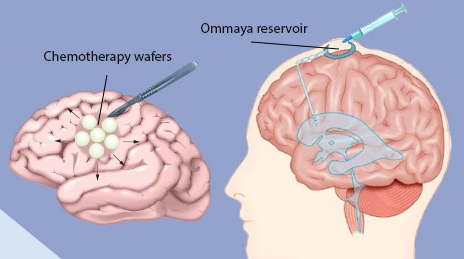
Chemotherapy for brain cancer is complex and depends heavily on several factors including the type of brain cancer (glioblastoma, meningioma, oligodendroglioma, etc.), the grade of the cancer (I-IV, with IV being the most aggressive), the patient's overall health, and the location and extent of the tumor. It's rarely used alone but is often part of a multi-modal treatment approach combining surgery, radiation, and targeted therapies.
Types of Chemotherapy Used:The specific chemotherapy drugs used vary depending on the cancer type and other factors. Commonly used agents include: - Temozolomide (Temodar): This is an oral alkylating agent frequently used for glioblastoma, often in combination with radiation therapy. It's relatively well-tolerated compared to other chemotherapy drugs.
- Carmustine (BCNU): This is a nitrosourea that can cross the blood-brain barrier (BBB) more effectively than some other chemotherapies. It's sometimes used for recurrent glioblastoma or other high-grade gliomas.
- Lomustine (CCNU): Another nitrosourea with similar properties to carmustine.
- Other Agents: Other chemotherapy drugs may be used, often in combination, depending on the specific circumstances. This can include platinum-based agents like cisplatin or carboplatin, though their use in brain cancer is less common due to challenges crossing the BBB.
Delivery Methods:- Oral: Some chemotherapy drugs, like temozolomide, are administered orally as pills.
- Intravenous (IV): Many chemotherapy drugs are given intravenously through an IV line.
- Intrathecal: This involves injecting the drug directly into the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) through a lumbar puncture. This method is used when the cancer has spread to the CSF.
Challenges in Treating Brain Cancer with Chemotherapy:- Blood-Brain Barrier (BBB): The BBB is a protective layer surrounding the brain that prevents many substances, including some chemotherapy drugs, from entering brain tissue. This makes it difficult to deliver effective doses of chemotherapy directly to the tumor.
- Side Effects: Chemotherapy drugs can cause a range of side effects, which can be more pronounced in patients with brain cancer due to the location of the tumor and the sensitivity of the brain. These side effects can include nausea, vomiting, fatigue, hair loss, neuropathy (nerve damage), and cognitive impairment.
- Drug Resistance: Cancer cells can develop resistance to chemotherapy drugs over time, limiting their effectiveness.
Chemotherapy is rarely used alone in the treatment of brain cancer. It's typically part of a multi-modal treatment strategy that may also include:- Surgery: To remove as much of the tumor as possible.
- Radiation Therapy: To kill cancer cells and shrink the tumor.
- Targeted Therapy: Drugs that target specific molecules or pathways involved in cancer growth.
- Supportive Care: This focuses on managing side effects and improving the patient's quality of life.
It is crucial to remember that this information is for general knowledge only and should not be considered medical advice. The best course of treatment for brain cancer should be determined by a qualified oncologist specializing in neuro-oncology. They will consider the patient's specific situation and create a personalized treatment plan.
Tags: BCNU Blood-Brain Barrier Brain Cancer CCNU Carmustine Lomustine Temodar Temozolomide  
|  1,288
1,288  0
0  0
0  3350
3350 