| Bone tumors are growths that develop in bone tissue, categorized as either benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous). Benign tumors are generally slow-growing, localized, and rarely spread to other parts of the body, often causing pain only if they press on nerves or other structures. In contrast, malignant bone tumors are aggressive, can spread (metastasize) to distant sites via the bloodstream or lymphatic system, and often present with more severe symptoms like pain, swelling, and bone fractures. While both types require medical attention and evaluation, malignant bone tumors pose a significantly greater threat to life and necessitate more extensive treatment, typically involving surgery, chemotherapy, and/or radiation therapy. 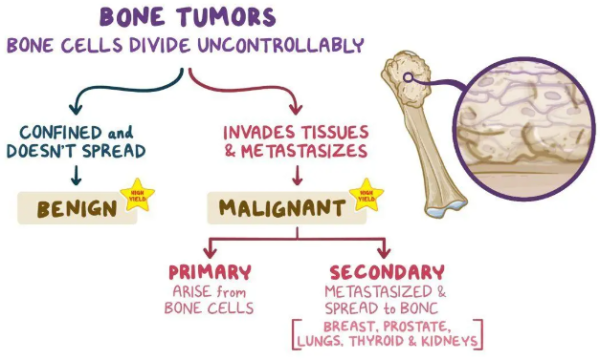
Bone tumors, growths within bone tissue, can be broadly classified as either benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous). Understanding their differences is crucial for appropriate diagnosis and treatment. Benign Bone Tumors:- Characteristics: Benign tumors are generally slow-growing, well-defined, and localized. They rarely spread to other parts of the body (metastasize). They often cause pain only if they press on nerves or other structures.
- Examples:
- Osteochondroma: The most common benign bone tumor, usually found near the ends of long bones. It's a cartilage-capped bony outgrowth.
- Enchondroma: A tumor composed of cartilage, often found in the hands and feet.
- Giant cell tumor: A relatively common benign tumor, but can be locally aggressive and potentially recur after surgery. Typically found near the ends of long bones.
- Fibrous dysplasia: A condition where normal bone is replaced by fibrous tissue. It can affect a single bone (monostotic) or multiple bones (polyostotic).
- Aneurysmal bone cyst: A fluid-filled cyst that expands the bone.
- Treatment: Treatment for benign tumors often involves observation, especially if asymptomatic. Surgery may be necessary if the tumor causes pain, fractures, or interferes with normal function. Some benign tumors may require regular monitoring via imaging.
Malignant Bone Tumors:- Characteristics: Malignant bone tumors are cancerous and aggressive. They grow rapidly, can invade surrounding tissues, and have the potential to metastasize (spread) to other parts of the body through the bloodstream or lymphatic system. They often cause pain, even early on.
- Examples:
- Osteosarcoma: The most common primary malignant bone tumor in children and young adults. It often affects the bones around the knee.
- Ewing sarcoma: A malignant tumor that typically affects children and young adults, often in the bones of the pelvis, legs, or arms.
- Chondrosarcoma: A malignant tumor arising from cartilage cells. It's more common in adults than osteosarcoma.
- Multiple myeloma: A cancer of plasma cells in the bone marrow. It doesn't typically present as a single mass but rather as multiple lesions throughout the skeleton.
- Treatment: Treatment for malignant bone tumors is complex and usually involves a combination of approaches:
- Surgery: To remove the tumor, possibly including limb salvage surgery (preserving the limb) or amputation.
- Chemotherapy: To shrink the tumor before surgery and to kill any remaining cancer cells after surgery.
- Radiation therapy: To kill cancer cells and reduce tumor size.
- Targeted therapy: To target specific molecules involved in cancer growth.
Diagnosis of bone tumors typically involves a combination of:- Physical examination: To assess symptoms and location of the tumor.
- Imaging studies: X-rays, CT scans, MRI scans, and bone scans to visualize the tumor and assess its extent.
- Biopsy: A tissue sample is taken and examined under a microscope to determine whether the tumor is benign or malignant and its specific type.
It is crucial to remember that this information is for general knowledge only. Accurate diagnosis and treatment planning require consultation with an orthopedic oncologist or other qualified medical professional. Self-diagnosis should be avoided. If you suspect a bone tumor, seek immediate medical attention.
Tags: Benign Tumors Bone Health Bone Tumors Cancer Awareness Cancer Treatment Healthcare Malignant Tumors Medical Conditions  
|  1,347
1,347  0
0  0
0  3350
3350 