Vulvar Intraepithelial Neoplasia as Risk Factors for Vulvar Cancerupdated at Nov 08, 2025 1,532 1,532 Vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia (VIN) represents the abnormal growth of cells within the vulvar epithelium.It's classified as a precancerous condition, |
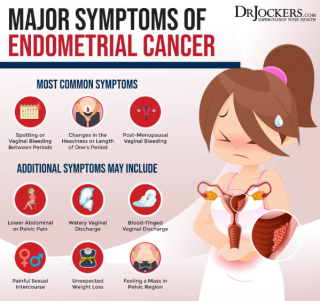
Can endometrial cancer be found early?created at May 05, 2009 1,278 1,278 Early detection of endometrial cancer is possible, |
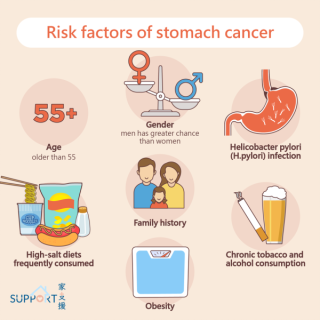
Understanding the Risks Between Aging and Stomach Cancercreated at May 04, 2009 1,306 1,306 The risk of stomach cancer increases significantly with age, |
How do you diagnose endocrine cancer?created at May 04, 2009 1,265 1,265 Diagnosing endocrine cancer typically involves a combination of physical examination, |
Understanding Vulvar Cancer Diagnosis: What to Expectcreated at May 05, 2009 1,345 1,345 Vulvar cancer is diagnosed through a combination of methods, |
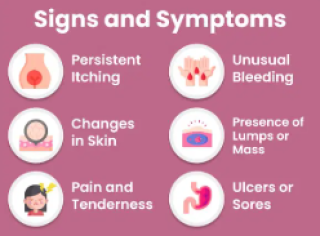
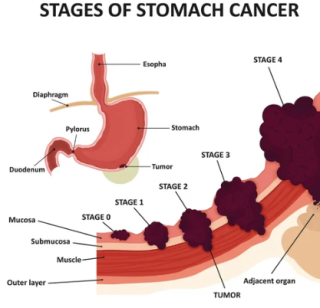
The basic information for Stomach cancercreated at May 03, 2009 1,399 1,399 Stomach cancer, |
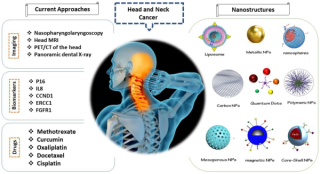
How will a physician make a diagnosis of head and neck cancer?created at May 09, 2009 1,237 1,237 Diagnosis of head and neck cancer typically begins with a thorough medical history and physical examination, |
Understanding the Diagnostic Process for Liver Cancercreated at May 04, 2009 1,409 1,409 If you’re concerned about liver cancer, |
Unveiling the Link: Human Papillomas (HPV Infection) as Risk Factors for Vulvar Cancercreated at May 05, 2009 1,320 1,320 Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection has emerged as a significant contributor to vulvar cancer, |
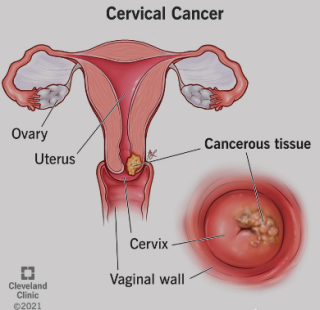
Decoding Diagnosis: Unraveling the Path to Detecting Cervical Cancercreated at May 04, 2009 1,441 1,441 Detecting cervical cancer involves a systematic approach, |
Decoding the Pelvic Exam: A Comprehensive Women's Health Assessmentupdated at Nov 14, 2025 1,372 1,372 A pelvic exam is a vital part of comprehensive women's healthcare.It involves a thorough evaluation of key reproductive organs. What a Pelvic Exam EntailsDuring a pelvic exam, |
How do I read my Pap smear results so that I can understand them?created at May 04, 2009 1,533 1,533 Results Description Follow-up Within Normal Limits No abnormal cells detected. Return for pelvic exam and Pap test in one year. Atypia Cells of Uncertain Significance ASCUS Some cells show a few chan... |
How is Hodgkin's disease diagnosed?created at May 22, 2009 1,600 1,600 If Hodgkin's disease is suspected, |
What is the difference between precancerous conditions and cancer of the cervix?created at May 04, 2009 1,280 1,280 Cells on the surface of the cervix sometimes appear abnormal but not cancerous. Scientists believe that some abnormal changes in cells on the cervix are the first step in a series of slow changes that can lead to cancer years later. That is, |
How will I be diagnosed for colorectal cancer?created at May 04, 2009 1,530 1,530 To find the cause of symptoms, |